Arrhythmia Detection
Problem Statement
Cardiovascular diseases, including cardiac arrhythmias, are a major health issue in low income countries, such as those in sub-Saharan Africa. Due to the lack of proper diagnostic equipment, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are the second leading cause of death in these parts of the world, accounting for nearly 35% of all annual deaths. Lack of access to hospitals with cardiac resources and trained personnel to diagnose cardiac arrhythmias are key contributing factors to the high death toll that cardiac diseases cause in these areas. The average cost of an electrocardiogram (ECG) in Cameroon is $180, which is 2.7 times higher than the average minimum monthly wage there. Furthermore, there are large populations of rural communities who may not have transportation capabilities to get the healthcare they need. This leaves hundreds of millions of people without access to the basic arrhythmia detection that is considered standard in most parts of the world.
In order to combat this problem, we are aiming to develop a low-cost and accessible method of cardiac arrhythmia detection that would address the needs of these communities. We propose a solution which consists of two parts: 1) a mobile app which uses a novel machine learning algorithm to detect cardiac arrhythmia and 2) a wearable device which utilizes an optical pulse sensor to collect data that can be converted into ECG data. The device will be designed such that patients may use it as an alternative to a Holter monitor, which is commonly used to record ECG data for long periods of time. From the ECG data collected by the device, the algorithm will be able to detect multiple types of arrhythmia.
Implementation
Neural Network
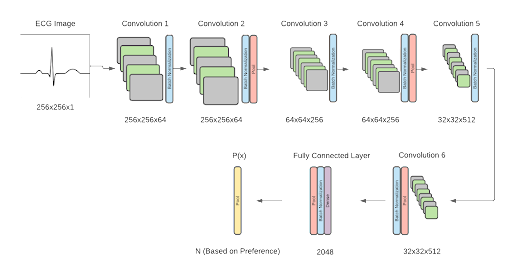
In order to categorize the patient’s ECG as normal or abnormal, a binary algorithm was created. The normal category indicates that the patient heartbeat is healthy and falls within the normal length between QRS indices, and the abnormal data tells the user that they may have a type of cardiac arrhythmia. The type of abnormality can further be specified by extending the algorithm to a multi-classification model, with 7 types of abnormalities defined (Premature Atrial Contraction, Premature Ventricular Contraction, Paced Beat, Right Bundle Branch Block Beat, Left Bundle Branch Block Beat, Ventricular Flutter Wave Beat, and Ventricular Escape Beat). The framework for the software was designed as shown below. The model structure utilizes a convolutional neural network algorithm, adapted from Jun’s ECG arrhythmia classification. The proposed binary classification model yielded an accuracy of 99.06%. Initial tests on multi classification of heartbeats using the proposed architecture yielded an accuracy of 98.95% accuracy.
Device
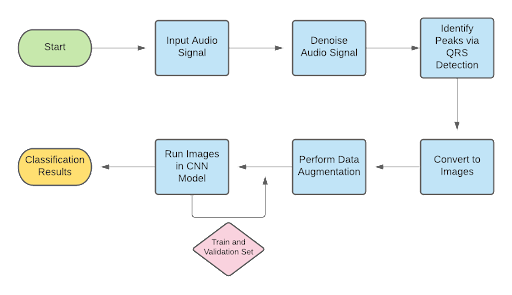
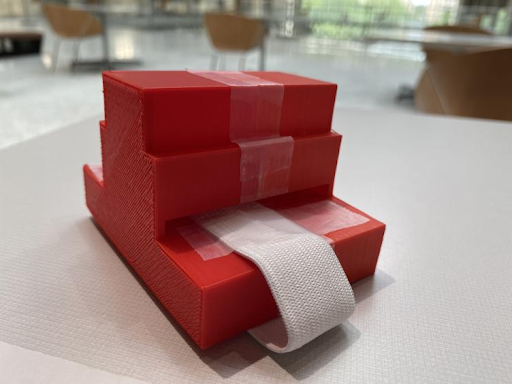
As a cheaper alternative to an ECG machine, an optical pulse sensor was used as the sensor to take heartbeat measurements for the prototype. An optical pulse sensor can collect pulse data which is then converted to an ECG signal using a process that has previously been used to convert piezoelectric sensor data to ECG data. An initial prototype is shown below.
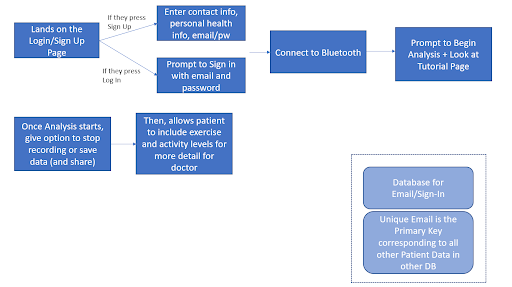
Mobile App
The designed algorithm was housed in the form of an app that would allow patients to easily access the features of the device and algorithm. The figure below represents the flow chart for the app.